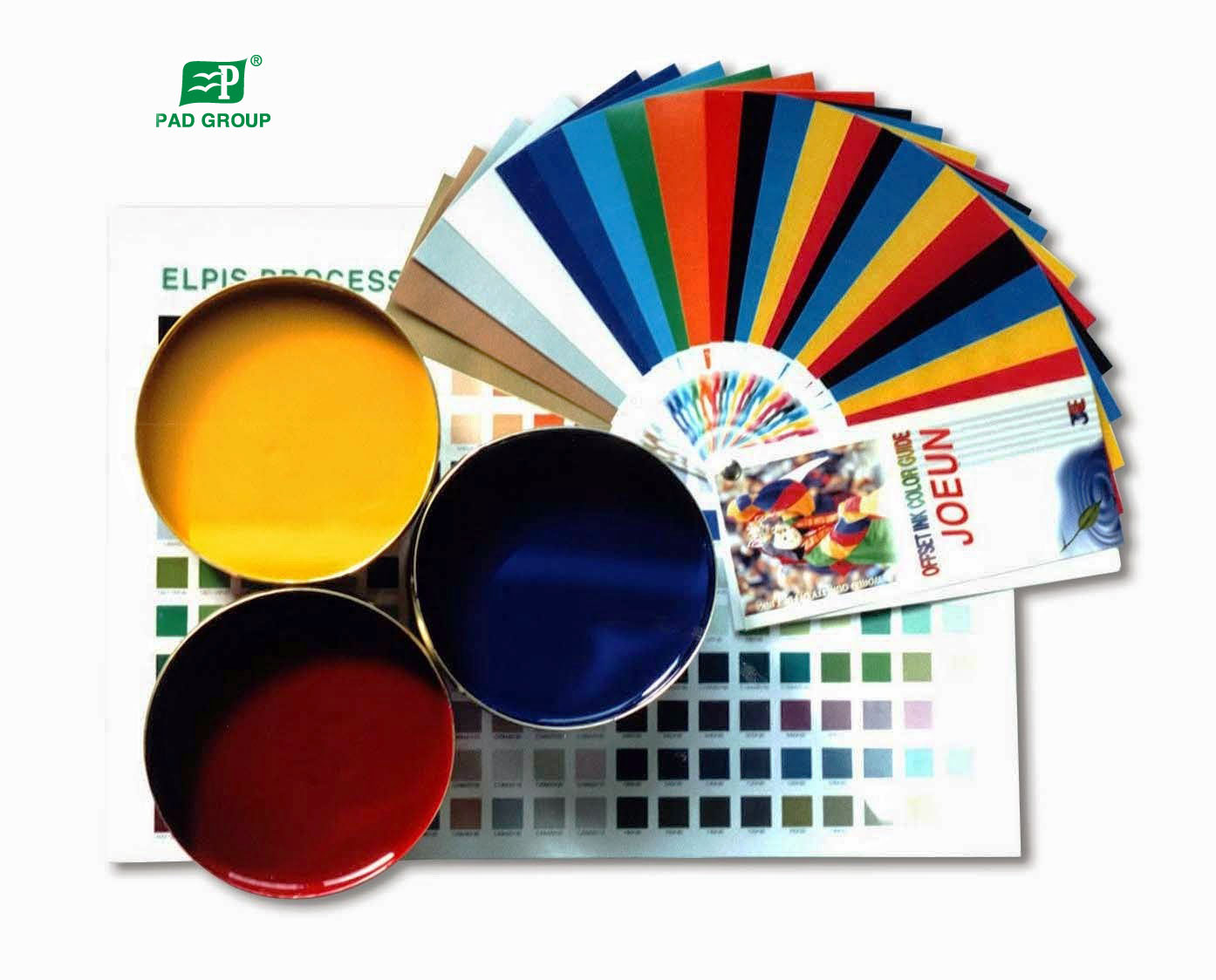
Some basics about the Offset printing industry
Offset printing, in itself, speaks for the meaning of the printing method whose name it bears. Offset means transmission. Offset printing is a flat printing, printed elements and non-printed elements are located on the same plane.

SOME BASIC FEATURES OF THE OFFSET PRINTING INDUSTRY
I. WHAT IS OFFSET PRINTING / WHAT IS OFFSET PRINTING
Offset printing, in itself, speaks for the meaning of the printing method whose name it bears. Offset means transmission. Offset printing is a flat printing, printed elements and non-printed elements are located on the same plane.
Today, Offset is the most popular printing method in the printing industry. Most recently, people invented the dry Offset printing method (waterless Offset), meaning the print does not need to be rubbed with water. The dry Offset printing method is based on the technique of cooling the plate tube and the printed plate has a lower printed element than the unprinted element. The non-printed element is made of silicone, the printed element is made of Photopolymer and is located about 2µm lower than the non-printed element. This method has the advantage of completely eliminating the effects that the moisturizing solution can cause during the printing process such as dot gain, paper stretching, and no need to pay attention to ink balance. - water...

1. Principle of Offset printing:
Offset printing is a flat and indirect printing method. Offset prints are coated with a photosensitive layer that absorbs ink. The unprinted element, when exposed to light, will be washed away, revealing the base layer. Printed elements that are not exposed to light will be retained. The image on the print is a positive image because it is indirectly transmitted through the rubber tube and then transferred onto the printing material. The printing element attracts ink and repels water, the non-printing element attracts water and repels ink. This is based on the surface tension of the wetting solution relative to the printing element (repelling water) and the non-printing element (receiving water) and the surface tension of the ink relative to the printing element (receiving ink) and the non-printing (ink ejecting) element of the print. The Zisman method states that if a liquid wants to cover the surface of a solid, it must have a surface tension lower than the surface tension of that solid. So, the wetting solution must have a surface tension lower than the surface tension of the unprinted element, and the ink must have a surface tension lower than the printed element. We also know that Offset printing ink is oil-based and very hydrophobic.
First, the Offset print is rubbed with water, the printing element repels water and the non-printing element receives water. After that, the Offset print continues to be rubbed by the ink roller, the printing element receives ink and the non-printing element (which has received water) pushes ink. After this cycle, the ink on the printing element of the Offset print mounted on the plate cylinder is transmitted through the rubber tube (blank cylinder). The rubber tube receives ink and transfers it to the paper through the printing pressure of the impression cylinder.

2. Basic structure of Offset printer:
Paper supply department: has the function of supplying paper one sheet at a time into the printing unit of the machine.
Pass tube: has the function of transferring paper from one printing unit to another.
Printing unit: has the function of transmitting from print to paper.
Endless chain: has the function of transferring paper from the last printing unit to the output table
Paper receiving unit: receives paper from the endless chain and stacks it neatly.

II. PRINT PRINTING OFFSET
Today, people often use two technologies in Offset printing:
- Computer To Film (CTF): technology that transfers data from a computer to film through film recorders. The film is placed on the print to be exposed to UV rays. After exposure, the print goes through the developing process to be installed on the printer. CTF technology has the disadvantage that prints are exposed manually, the accuracy is not high, it is easy to increase the level, lose trace....
- Computer To Plate (CTP): technology that transfers data from a computer to printed copies directly through a plate recorder. After being recorded, the printout goes through the printing process and is then installed on the printer. CTP technology has the advantage of sharp, accurate printing, eliminating the defects of CTF technology.
III.POST PRINTING TECHNOLOGY
After printing, the printed material is sent to the post-printing production stage. This is the stage of completing the product. Depending on the nature of the goods and the requirements of the order, the post-printing steps may be more or less, may follow this process but may also follow another process. The post-printing process includes many stages. Depending on the customers and products the printer targets, the printer will invest in which post-printing steps. However, basically, post-printing technology includes the following steps:
- Cut: cut the product to the correct size or divide multiple products on one printed sheet. Most printed products have to go through this stage, the equipment used is a single-sided cutting machine. For book products, a 3-sided cutting machine is often used. When designing products, it is necessary to take into account the appropriate cropping allowance, usually 3mm.
- Gloss lamination: can be PE, OPP, BOPP lamination..., or Varnish coating. Popular varnishes today are UV and Waterbased. The drying mechanism of Vanish UV is under the influence of UV rays (ultra violet), the drying mechanism of Varnish Waterbased is under the influence of heat (IR). Varnish can be coated in-line (if the printer has a coating unit) or off-line (coated with a specialized Varnish coating machine after printing). After coating with Varnish Waterbased, depending on order requirements, people can put it through a Calendering machine to increase the gloss of the Varnish Waterbased layer.
- Optical refraction: processing the surface of materials to print very small patterns that cannot be done by negative-positive binding. Commonly used for printing materials is metallized laminated paper.
- Filling: is the step of joining two layers of materials together. Can be paper-paper, or paper-carton.
- Crimping and die-cutting: is the step of shaping the product into the desired shape.
- Window stickers: Often used for paper boxes. The product is wrapped in a window box, then glued to a suppor sheet, so that the user can observe the product contained inside.
- Pasting: the product is a box or paper bag, after going through the folding and closing process, the finished product will be glued.
- Folding: products are books, magazines... before being bound, they are put through a folding machine. Depending on the product, it can be folded 1 line, 2 lines, 3 lines...
- Binding: can be binding with glue or staples.
- Injection needle
Currently, with the trend of developing offset printing technology, the limitation of pixel sophistication has been overcome, printing is not only printed on paper but also printed on materials with good flat surfaces and surface treatment. face.
In the Pacific, with more than 20 years of experience in the packaging industry, starting from 2016 and 2017, we continued to develop the plastic printing segment with the birth of a generation of beautiful Offset printed plastic lanterns. Mid-Autumn Festival lanterns printed on virgin PP plastic, shaped by suction plastic, corrugated Carton, Offset packaging are the shaping of a closed chain of the packaging field in general at Pacific Packaging Corporation.
Edited by Andy Hieu ( Nam Rice Founder )
Be responsible about content: Dinh Xuan Duy
PadGroup Team